On January 13, 2016, Dr. Xin-Hua Feng’s laboratory published a paper online entitled “Loss of a-Tubulin Acetylation is Associated with TGF-b-induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition” in Journal of Biological Chemistry. Dr. Gu is the first author of the paper and Dr. Feng is the corresponding author.
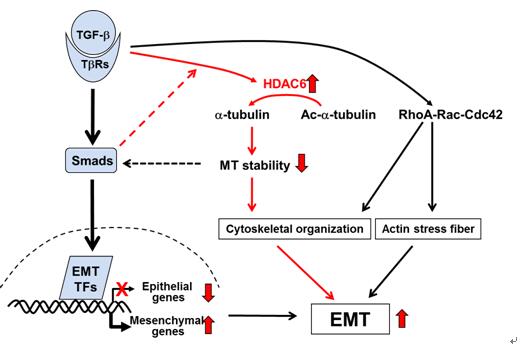
The epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) is a process by which differentiated epithelial cells reprogram gene expression, lose their junctions and polarity, reorganize their cytoskeleton, increase cell motility and assume a mesenchymal morphology. Despite the critical functions of the microtubule (MT) in cytoskeletal organization, how it participates in EMT induction and maintenance remains poorly understood. Here we report that acetylated α-tubulin, which plays an important role in microtubule (MT) stabilization and cell morphology, can serve as a novel regulator and marker of EMT. A high level of acetylated α-tubulin was correlated with epithelial morphology and it profoundly decreased during TGF-β-induced EMT. We found that TGF-β increased the activity of HDAC6, a major deacetylase of α-tubulin, without affecting its expression levels. Treatment with HDAC6 inhibitor tubacin or TGF-β type I receptor inhibitor SB431542 restored the level of acetylated α-tubulin and consequently blocked EMT. Our results demonstrate that acetylated α-tubulin can serve as a marker of EMT and that HDAC6 represents an important regulator during EMT process.
Text link:http://www.jbc.org/content/early/2016/01/13/jbc.M115.713123.long



